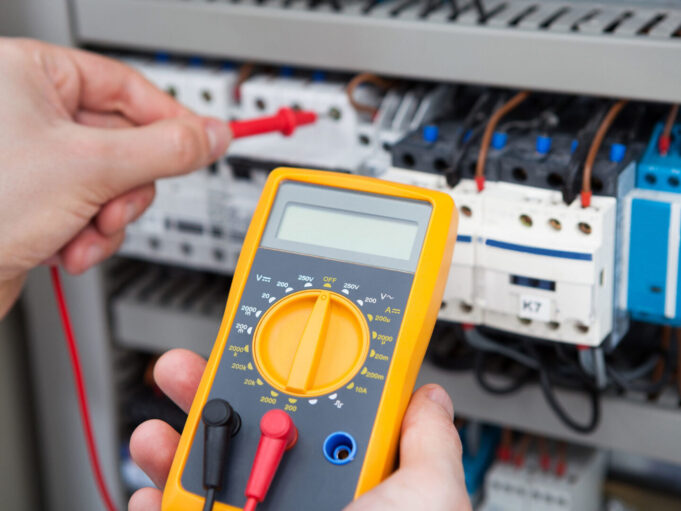
In a world that thrives on electricity, electrical equipment plays a pivotal role in our daily lives. From powering our homes to driving industries, electrical equipment is an indispensable part of modern civilization. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical equipment is paramount.
This is where electrical equipment testing and tagging step in. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of electrical apparatus assurance, exploring its importance, regulatory aspects, trial methods, and best practices.
Electrical equipment is a double-edged sword. While it powers our lives, it also poses serious risks if not properly maintained and monitored. Faulty electrical equipment can lead to fires, electric shocks, and costly downtime in industries. This is why electrical equipment testing and tagging are essential for both residential and commercial settings.
The Basics of Electrical Equipment Testing
At its core, electrical equipment testing is the systematic process of evaluating the condition and safety of electrical appliances and machinery. Its primary purpose is to identify and rectify faults and defects before they escalate into hazardous situations.
Through trial, potential risks can be mitigated, and the lifespan of the apparatus can be extended.
Electrical equipment comes in a myriad of forms, ranging from small household appliances to massive industrial machinery. All these devices, irrespective of size and purpose, should undergo regular testing and tagging.
This includes but is not limited to, power cords, extension leads, power boards, and machinery in commercial settings. If you’re living in the land down under and require this type of service you need to check out, test and tag Sydney.
Regulatory Compliance

To ensure uniformity and safety, various regulations and standards govern electrical equipment trial and tagging. These standards are established by authorities such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) globally.
Understanding these regulations is crucial for businesses and individuals to comply with the law and ensure the safety of users.
Businesses, in particular, have a legal responsibility to ensure their electrical apparatus meets the required standards. Failing to do so can result in legal repercussions, including fines and, in extreme cases, imprisonment. Compliance is not just about adhering to the law; it’s about safeguarding lives and property.
Frequency of Testing
The frequency of electrical equipment testing varies depending on several factors, including the type of apparatus, its usage, and the environment in which it operates. While some equipment may need a trial every few months, others can go longer between inspections.
Knowing when to test is critical in maintaining safety and preventing unexpected failures.
Factors such as the age of the equipment, the level of risk associated with its use, and its history of faults should be considered when determining the tryout frequency. Regular inspections help in identifying patterns and trends that can guide decisions regarding maintenance and replacement.
Testing Methods
Electrical equipment testing employs various methods, each designed to assess specific aspects of apparatus safety. Visual inspection, for instance, is the simplest form of testing, focusing on external conditions.
Portable Appliance Testing (PAT), on the other hand, involves a more comprehensive assessment, including electrical trials. Understanding when and how to use these methods is crucial for effective testing.
Choosing the right testing method depends on the type of equipment, its usage, and the potential risks associated with it. Visual inspections are suitable for everyday household appliances, while PAT tryouts are essential for commercial and industrial apparatus. The method employed should align with the equipment’s risk profile.
In the comprehensive overview of testing and tagging electrical equipment, it’s essential to remember the expert advice from professional electricians when rewiring your home, ensuring safety and compliance with best practices.
The Role of Tagging

Equipment tagging is an integral part of the testing process. Tags provide vital information about the equipment’s testing date, the technician responsible, and whether it passed or failed. These tags act as a visual cue, ensuring that users are aware of the equipment’s condition and the need for periodic trials.
A well-designed equipment tag includes details such as the test date, the next due date for testing, a unique identification number, and the technician’s name or identification. This information helps in tracking the equipment’s history and facilitates timely retesting.
Testing Equipment and Tools
Effective electrical apparatus trials require a range of specialized tools and equipment. Multimeters, insulation testers, and earth leakage testers are some of the essential tools used by technicians. Each tool serves a specific purpose in assessing the equipment’s safety and functionality.
Using the right tools is not just a matter of convenience; it is essential for accurate testing. Using inappropriate or outdated tools can lead to incorrect assessments, potentially putting lives and property at risk.
DIY vs. Professional Testing
Deciding between DIY testing and hiring professionals is a critical choice that individuals and businesses must make. DIY tryouts may seem cost-effective, but it comes with risks. Professionals, on the other hand, bring expertise and advanced tools to the table.
Choosing between DIY and professional testing depends on factors like the type of apparatus, available resources, and the level of expertise. While simple visual inspections can be done by anyone, complex machinery, and electrical systems are best left to trained professionals.
Importance of Record-Keeping
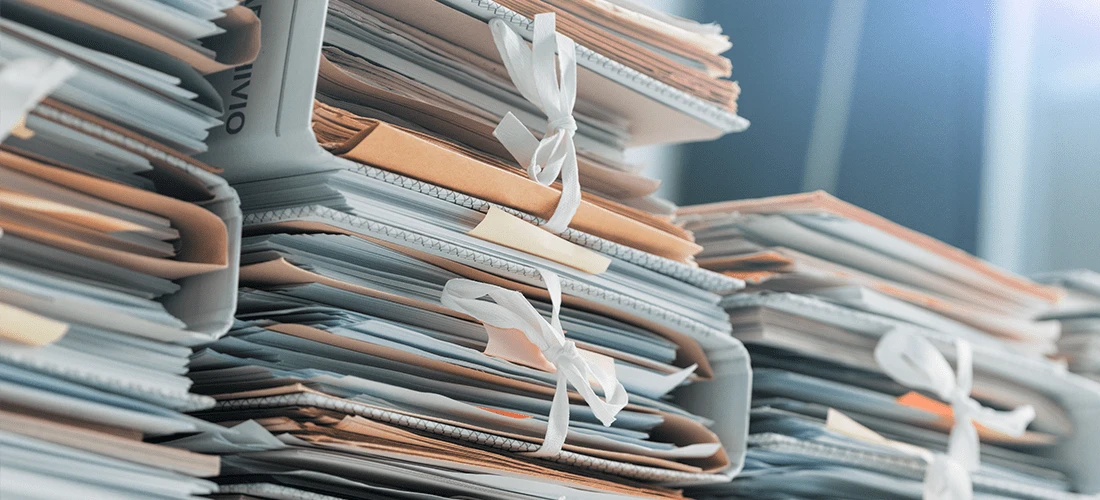

Maintaining comprehensive records of electrical equipment testing and tagging is more than just good practice; it’s a necessity. These records serve as a historical account of apparatus maintenance and can be invaluable in demonstrating compliance and safety.
Detailed records provide a paper trail that can be presented to regulatory authorities to prove compliance with standards and regulations. Additionally, in case of accidents or failures, these records can be instrumental in investigations and insurance claims.
Common Electrical Equipment Failures
Electrical equipment is susceptible to various faults and failures, including frayed cords, loose connections, and insulation breakdown. Regular testing helps in detecting these issues early, preventing accidents and costly downtime.
Identifying and rectifying common electrical apparatus issues before they escalate is not just about safety; it’s also about saving money and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Training and Certification
Proper training is essential for individuals involved in electrical equipment testing and tagging. Training programs provide the necessary knowledge and skills to carry out testing effectively and safely.
Certification adds credibility to an individual’s expertise. Programs such as the Certified Appliance Tester (CAT) program and the Certified Electrical Safety Worker (CESW) program offer recognized certifications in this field.
When considering the protection of your valuable electronic assets, it’s essential to delve into the details of insurance for electronic equipment, which is comprehensively covered in the related article.
Best Practices and Conclusion
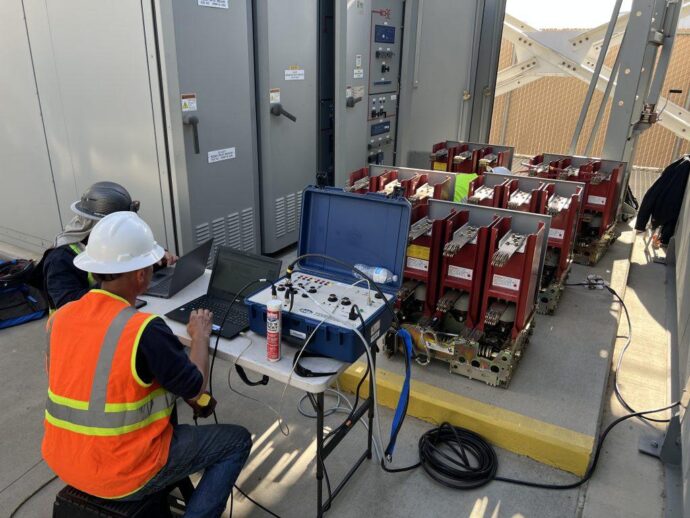

Summarizing the key best practices for electrical apparatus testing and tagging, including regular inspections, using appropriate tools, and maintaining detailed records.
In conclusion, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical equipment through testing and tagging is not just a legal requirement; it’s a commitment to safeguarding lives and property. The investment in apparatus assurance pays off in the form of reduced risks, fewer accidents, and uninterrupted operations.