Whether you’re considering a DIY project or looking to gain knowledge before hiring a professional, understanding the basics of electrical wiring is the first step toward a successful home rewiring project. The fundamentals are relatively simple: the power comes into your home from a supply company, travels through an electrical meter to measure your consumption, then feeds into your home’s main electrical panel where it’s divided into separate circuits. Each circuit is protected by a circuit breaker, designed to trip in case of an overload or short circuit.
What many people don’t realize is the importance of distinguishing between different types of wires. Primarily, there are three wires: hot, neutral, and ground. The hot wire (usually red or black) carries power from your service panel to your outlets and appliances.
The neutral wire (typically white) returns the current back to the Electric Control Panels, and the ground wire (usually green or bare) provides a safe path for electricity in case of a fault. Understanding these basics equips you with the knowledge to carry out informed conversations with an electrician and ensure your wiring conforms to standard safety procedures.
Ensuring Electrical Safety: Codes and Regulations
Safety is paramount when dealing with electricity, and there are codes and regulations designed to ensure it. The National Electrical Code (NEC) is the widely adopted standard in the U.S. It provides guidance on safe electrical design, installation, and inspection to protect people and property from electrical hazards. It’s important to note that while the NEC is a federal law, it’s usually enforced at the local level, and some states or municipalities may have additional requirements.
Electrical safety extends beyond codes and regulations. It’s about fostering safe practices, such as turning off the power before working on any electrical components and using insulated tools. You also need to ensure all equipment and appliances are in good working order and free from damage. Damaged cords, plugs, or equipment can pose serious risks, leading to electric shock or fire.
Lastly, ensuring safety involves maintaining your home’s electrical system. Regular inspections can help you identify potential hazards before they become problems. This includes checking your electrical panel for signs of corrosion or overheating, testing your outlets for proper grounding, and examining cords and appliances for wear or damage. Your home’s safety depends on the health of your electrical system.
Planning Your Home Rewiring Project
Before you start your rewiring project, take the time to map out your existing electrical system. This can help you understand where changes need to be made and anticipate potential challenges. Be mindful of your family’s power consumption habits: identify the devices that need more power, rooms that require more outlets, or areas where you would benefit from having controlled lighting.
The next step is to consider the future. Your rewiring project should account for changes in technology and your lifestyle. For instance, you might want to add dedicated circuits for home automation systems or electric vehicles. You may also need to consider adding more power points in a home office or upgrading the wiring in your kitchen to accommodate new appliances. Remember, your goal is not just to satisfy your current electrical needs but also to future-proof your home.
Finally, work out a timeline and budget. Rewiring can be a large and disruptive project, so it’s crucial to plan carefully to minimize inconvenience. Outline the scope of work and seek multiple quotes from professionals to estimate costs. A well-planned rewiring project not only increases the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system but also adds to your property’s value.
Choosing the Right Wiring Materials and Components

Copper wiring is a popular choice for home wiring due to its excellent conductivity and heat resistance. Still, aluminum can be a cost-effective alternative for larger feed wires that bring electricity into the home. Ensure that the wire gauge, or size, is appropriate for the current it will carry; typically, a 15-amp circuit uses 14-gauge wire, while a 20-amp circuit uses 12-gauge.
When it comes to outlets, grounded three-prong outlets are the standard for modern homes. They provide a path for electrical energy to travel safely to the ground in case of a fault. GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets are required in areas where water is present, like bathrooms and kitchens, as they can shut off power if a ground fault is detected. USB outlets might be a desirable upgrade in rooms where you charge electronic devices.
For light switches, consider where you may benefit from dimmers or three-way switches. Dimmers allow you to adjust the light intensity, adding ambiance and energy efficiency. Three-way switches are useful in larger rooms or corridors, allowing you to control lighting from two locations. Choosing the right components isn’t just about functionality, but also about enhancing comfort and convenience in your home.
Rewiring Techniques for Different Areas of Your Home
Different areas of your home have different electrical needs, and understanding these can help you plan your rewiring project effectively. The kitchen, for example, typically requires multiple circuits to accommodate all the appliances. It’s also beneficial to have GFCI outlets near the sink to prevent electrical shock.
Your living room might need more outlets to cater to entertainment systems, and you might want to consider adding dimmer switches for lighting control. For bedrooms, ensure there are enough outlets for lamps, electronics, and possibly a ceiling fan. Bathrooms also require GFCI outlets, and you might want to add dedicated circuits for high-wattage devices like hair dryers.
Outdoor wiring requires special consideration. Exterior outlets should be GFCI protected and have weatherproof covers. Consider whether you need circuits for outdoor lighting, a pool or spa, or an outdoor kitchen. Each of these areas has unique requirements, so you need to consider your specific needs when planning your rewiring project.
Upgrading Your Electrical Panel and Circuit Breakers
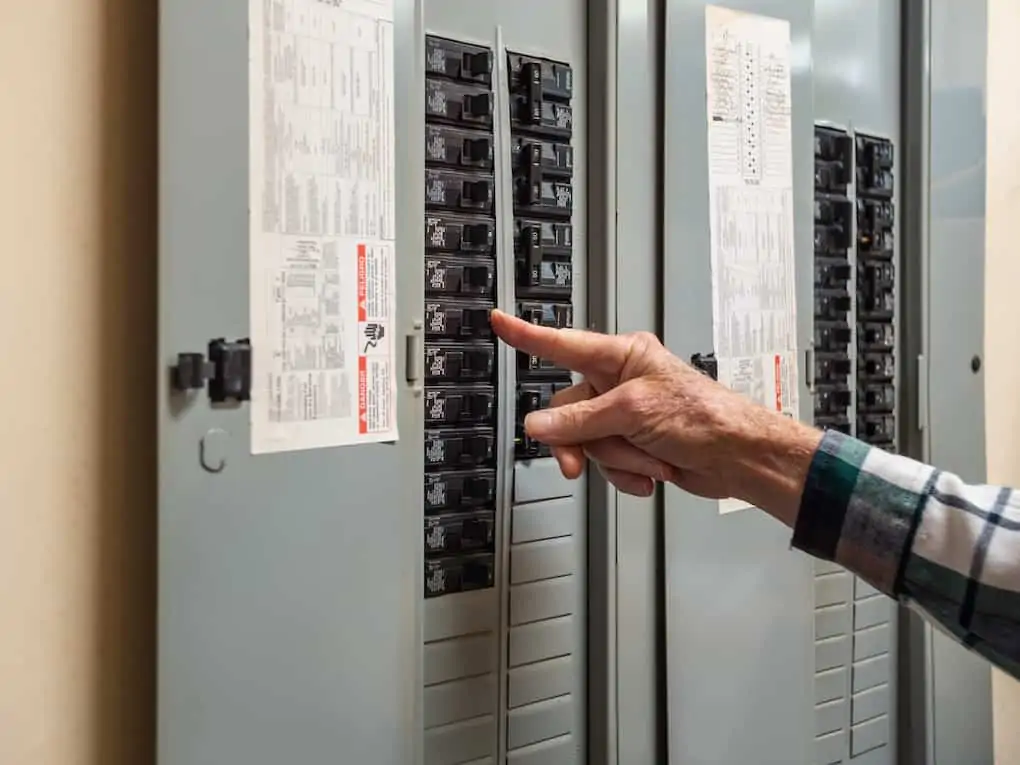

If your home is older, one of the key components you might need to upgrade during a rewiring project is your electrical panel. Modern households often have higher electricity demands, and an old panel may not be able to handle the load, causing frequent breaker trips. A new panel can increase your home’s electrical capacity, allowing for more circuits and improving overall safety and efficiency.
Circuit breakers are another crucial component to consider. They are designed to protect your home by tripping and cutting power when they detect an overload or short circuit. When upgrading your panel, it’s typically a good idea to replace any old or damaged breakers to ensure they function correctly. You might also want to consider installing arc-fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs), which provide enhanced protection by detecting potential fire-causing arcs.
Remember, upgrading your electrical panel is a job for professionals. It involves working directly with the main power line, and any mistakes can lead to serious injury or property damage. Always hire a licensed electrician for this task.
Conclusion
Rewiring your home can be a daunting task but it doesn’t have to be. With tips from professional electricians, you can easily and safely upgrade your electrical wiring system without spending too much time or money. Hopefully, this article has given you the knowledge and confidence to get started rewiring your home today!















